Representative Research Publications
Proteomic Analysis of Urothelium of Rats with Detrusor Overactivity Induced by Bladder Outlet Obstru 2018 > Representative Research Publications > Research Results Home
Proteomic Analysis of Urothelium of Rats with Detrusor Overactivity Induced by Bladder Outlet Obstruction
- Molecular and Cellular Proteomics / 2018 May
- Kim, Gun Hwa (Corresponding author)
Study Summary
Overactive bladder (OAB) syndrome is a condition that has four symptoms: urgency, urinary frequency, nocturia, and urge incontinence and negatively affects a patient's life. Recently, it is considered that the urinary bladder urothelium is closely linked to pathogenesis of OAB. However, the mechanisms of pathogenesis of OAB at the molecular level remain poorly understood, mainly because of lack of modern molecular analysis. The goal of this study is to identify a potential target protein that could act as a predictive factor for effective diagnosis and aid in the development of therapeutic strategies for the treatment of OAB syndrome.
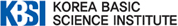
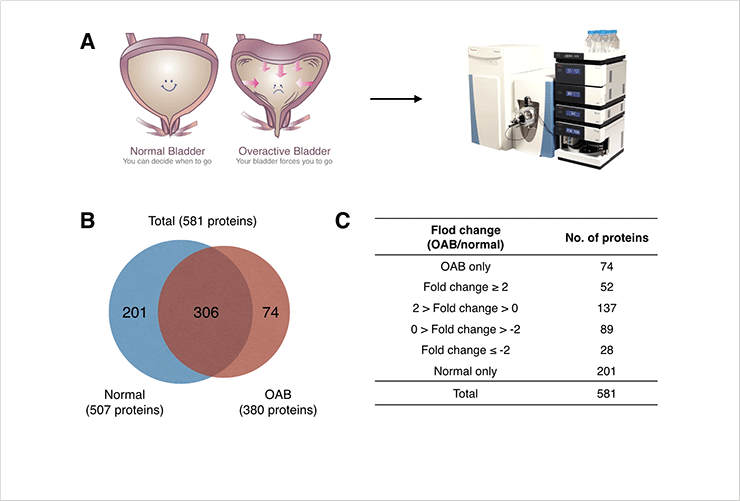 Figure 1. (A) Schematic illusration of proteomic study. (B) Venn diagram that shows the number of identified proteins from normal and OAB urothelium. (C) Quantitative analysis proteins expressed in urothelium.
Figure 1. (A) Schematic illusration of proteomic study. (B) Venn diagram that shows the number of identified proteins from normal and OAB urothelium. (C) Quantitative analysis proteins expressed in urothelium.
We produced OAB in a rat model and performed the first proteomic analysis on the mucosal layer (urothelium) of the bladders of sham control and OAB rats. The resulting data revealed the differential expression of 355 proteins in the bladder urothelium of OAB rats compared with sham subjects. Signaling pathway analysis revealed that the differentially expressed proteins were mainly involved in the inflammatory response and apoptosis. Our findings suggest a new target for accurate diagnosis of OAB that can provide essential information for the development of drug treatment strategies as well as establish criteria for screening patients in the clinical environment.
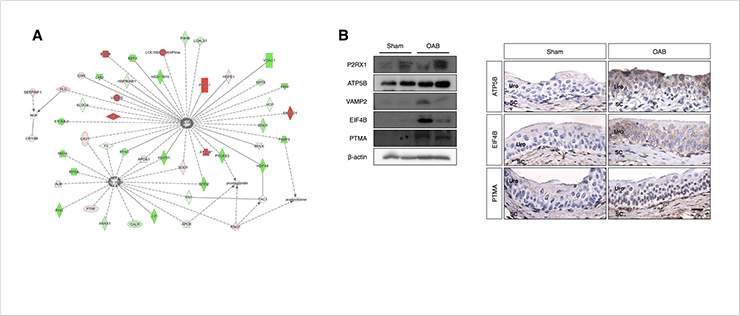 Figure 2. (A) Protein network analysiswith signaling molecules released from the urothelium. (B) Validation of upregulated proteins in OAB
Figure 2. (A) Protein network analysiswith signaling molecules released from the urothelium. (B) Validation of upregulated proteins in OAB