Representative Research Publications
2017 > Representative Research Publications > Research Results Home
Novel discovery of the survival mechanism of metastatic cancer cells
- Nature Communications / 2017 February
- Hwang, Geum Sook (corresponding author)
Study Summary
The present study elucidated the mechanism through which metastatic cancer cells survive and modify their metabolic pathways, for the first time in the world.
In particular, the study confirmed for the first time that cancer cells attack surrounding tissues, and spread from the initial organs and infiltrate other tissues through blood and lymphatic vessels (metastasis) by suppressing a metabolite (PFKP*) using a specific protein (Snail*), thereby regulating their own metabolism.
In other words, it was found that cancer cells gain reducing power favorable for survival by suppressing PFKP, which acts as a switch between aerobic glycolysis and the pentose phosphate pathway.
The present study used the metabolite analysis platform technology established at the Korea Basic Science Institute (Western Seoul Center) to observe major metabolites of cancer cell metabolic pathways; particularly, the SPE-800 MHz nuclear magnetic resonance mass-spectroscopy system, which was designated as the main research equipment, was used.
 Figure 1. The SPE-800 MHz NMR-MS system used in this study
Figure 1. The SPE-800 MHz NMR-MS system used in this study
Expected Effects
As the first report on the regulation of metabolism in metastatic cancer cells, the present study confirmed that metastatic cancer cells, in contrast to proliferating cancer cells, survive by regulating metabolism in directions that particularly promote catabolism. The results, which evinced new targets for metabolic therapy, are expected to provide evidence for the application of existing metabolic drugs targeting metabolic pathways in the treatment of cancer.
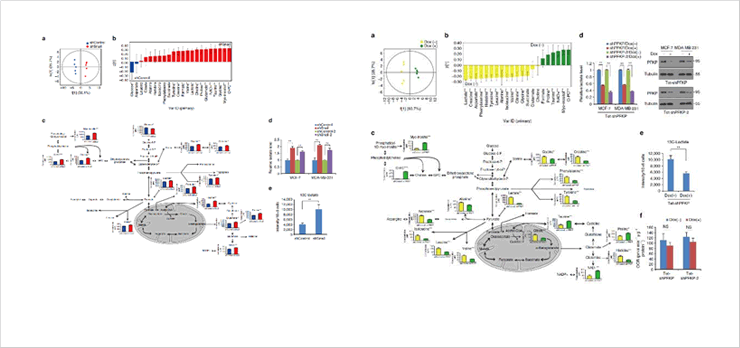 Figure 2. Metabolites and metabolic pathways in cancer cells measured through the metabolite analysis platform technology
Figure 2. Metabolites and metabolic pathways in cancer cells measured through the metabolite analysis platform technology