Representative Research Publications
Selective Electroncatalytic Reduction of Nitrite to Dinitrogen Based on Decoupled Proton-Electron Tr 2018 > Representative Research Publications > Research Results Home
Selective Electroncatalytic Reduction of Nitrite to Dinitrogen Based on Decoupled Proton-Electron Transfer
- Journal of the American Chemical Society / 2018 February
- Kim, Sun Hee (Corresponding author)
Study Summary
Development of selective electrocatalysts for the reduction of nitrite to dinitrogen utilizing sequential proton-electron transfer pathway. (In collaboration with professor Nakamura team at RIKEN in Japan)
The development of denitrification catalysts is important for sustaining the nitrogen cycle. However, because of involvement of complex multielectron/protons controlling the selectivity is difficult. To overcome this problem, we utilized sequential proton-electron transfer pathways. As a result, we achieved the highest Faradaic efficiency for detrification to date under neutral conditions. We identified the intermediate species by using EPR spectroscopy during the reactions.
In this report, we use CW/Pulse EPR system at Western-Seoul Center, KBSI to investigate the intermediates during denitrification reaction pathways.
Expected Effects
We successfully replicated in an artificial system through an sequential proton-electron transfer as seen in microbial denitrification. Thus, the concept of sequential proton-electron transfer pathways can be utilized for designing electrocatalttuc systems with many competing reaction pathways such as CO2 reduction.
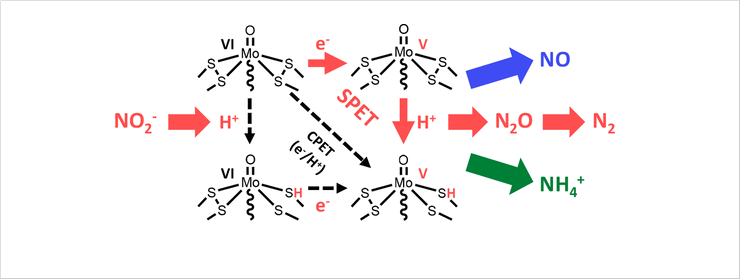 Figure 1. Schematic representation of the reaction pathway utilizing the electrocatalyst for denitrification.
Figure 1. Schematic representation of the reaction pathway utilizing the electrocatalyst for denitrification.