Representative Research Publications
Highly efficient electrochemical detection of hazardous materials 2019 > Representative Research Publications > Research Results Home
Highly efficient electrochemical detection of hazardous materials
- ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. / February 2019
- Yeonho Kim (1st author), Hae Jin Kim (Corresponding author)
Study Summary
Development of a low-cost electrochemical sensor
capable of highly sensitive detection of toxic phenols.
Gold (Au) was used as a catalyst for the detection of phenols. In this study, we fabricated heterostructure catalysts of Au/ZnS, which show increased detection sensitivity 25 times more than semiconductor catalysts alone.
The gold nanoparticles are directly dressed onto the surface of ZnS by the photodeposition process. The process is conducted in a wet chemical environment. Gold precursor is put into the ZnS containing solution under light irradiation, which is an environmentally friendly process.
When catalysts react with the toxic materials of phenol derivatives, they give out the electrons to the phenols. The working principle of the electrochemical sensor is reading the current value from the oxidation/reduction reaction in the targeted solution.
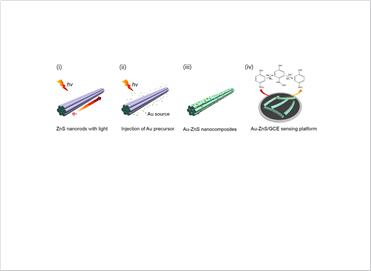 Figure 1. Schematic illustration of Au/ZnS catalysts via photodeposition process, and used as for the electrochemical sensor.
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of Au/ZnS catalysts via photodeposition process, and used as for the electrochemical sensor. 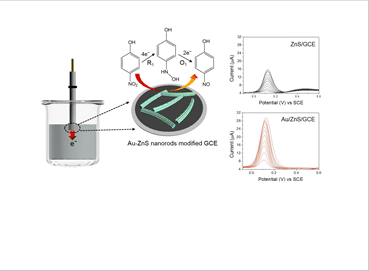 Figure 2.
Detection of the toxic substance phenol by an electrochemical method using the electron transfer between the semiconductor/metal catalyst.
Figure 2.
Detection of the toxic substance phenol by an electrochemical method using the electron transfer between the semiconductor/metal catalyst.
Expected Effects
It is expected that a new composite material capable of replacing expensive noble metal catalysts will be possible and commercialization of small electrochemical sensors capable of detecting toxic materials immediately in the field will be possible.
ㅇ DOI : https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b05603