Representative Research Publications
Schwann cells guide nerve regeneration through a detour route following peripheral nerve injuries 2019 > Representative Research Publications > Research Results Home
Schwann cells guide nerve regeneration through a detour route following peripheral nerve injuries
- J. Comp. Neurol. / June 2019
- Hyuno Kang (First & Corresponding author)
Study Summary
Dr. Hyuno Kang in Korea Basic Science Institute (KBSI), teamed up with Prof. Wesley Thomson in Texas A & M University, have found that Schwann cells not only help regenerations of nerve through their original pathways after injury but also reconstitutions of denervated synaptic sites thought the alternative bypassing routes. They used genetically modified mice expressing fluorescent proteins of unique colors in different cell types and monitored dynamic intercellular interactions in real time using live animals with a fluorescence microscope.
Sarcopenica is the degenerative loss of skeletal muscle mass, quality, and strength associated with aging and a major problem in many modern societies. Synaptic repair mechanism by detour route is helpful for rapid recovery but gives rise to increases in motor unit size if repeated, then, can cause sarcopenia paradoxically. Intravital multiphoton microscopy is expected to play an important role in implementing in vivo imaging to better understand life phenomena and find a solution for life threatening diseases.
Hyuno Kang, Le Tian and Wesley J. Thompson (2019) Schwann cell guidance of nerve growth between synaptic sites explains changes in the pattern of muscle innervation and remodeling of synaptic sites following peripheral nerve injuries. Journal of Comparative Neurology, 527(8):1388-1400. DOI: 10.1002/cne.24625
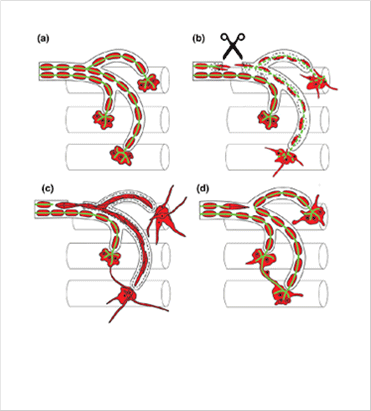 Schwann cells (red) guide nerve (green) regeneration through a detour route following nerve injuries
Schwann cells (red) guide nerve (green) regeneration through a detour route following nerve injuries In vivo imaging with Intravital Multiphoton Microscope
In vivo imaging with Intravital Multiphoton Microscope