Representative Research Publications
Development of optical imaging probe for stimulated activity in hepatocellular carcinoma 2017 > Representative Research Publications > Research Results Home
In vivo imaging of b-galactosidase stimulated activity in hepatocellular carcinoma using ligand-targeted fluorescent probe
- Journal : Biomaterials (2017. 04.)
- Equipments : IVIS Spectrum System
Authors
Eun-Joong Kim (1st author, KBSI), Rajesh Kumar (Korea Univ), Amit Sharma (Korea Univ), Byungkwon Yoon (Korea Univ), Hyun Min Kim (KBSI), Hyunseung Lee (KBSI), Jong Seung Kim (Korea Univ)
Abstract
We developed a noninvasive fluorescent probe (DCDHF-βgal) for the sensitive detection, and in vivo visualization of β-galactosidase in hepatocyte HepG2 cells and its xenograft model. As a model system for in vivo targeted imaging, DCDHF-βgal possessing galactose units selectively target hepatocyte and monitor the β-galactosidase activity with deep tissue penetration and low background interference. DCDHF-βgal was activated by intracellular β-galactosidases as the driving force for the release of NIR fluorophore, thereby exhibiting a ratiometric optical response. Initial fluorescence emission measured at 615 nm was changed to fluorescence at 665 nm upon activation of DCDHF-βgal with β-galactosidase. Ratiometric fluorescence detection of βgal was also observed in hepatocellular carcinoma cells and tumor xenograft. The noninvasive in vivo optical imaging facilitated by a targeted and enzyme-activated imaging agent would be useful in various biomedical and diagnostic applications.
Expected Contribution to Science & Technology
These findings provide a new application tool for the development of bioimaging techniques to detect cancer-cell-specific overexpressed enzymes.
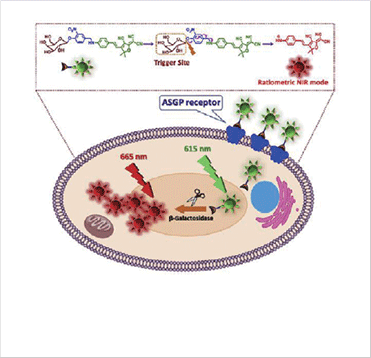 Schematic illustration of NIR probe for the detection of βgal enzyme
Schematic illustration of NIR probe for the detection of βgal enzyme
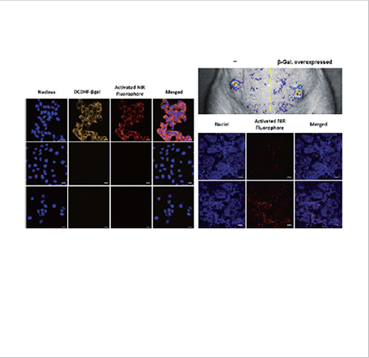 In vitro (left) and in vivo (right) results for the detection of βgal enzyme
In vitro (left) and in vivo (right) results for the detection of βgal enzyme